Rules-Based Money Management Part 2: Measuring the Market
In the realm of finance, money management is an essential aspect of achieving financial success. Establishing a rules-based approach to money management can help individuals navigate the complexities of the market with more discipline and structure. In this article, we will delve into the significance of measuring the market as part of a rules-based money management strategy.
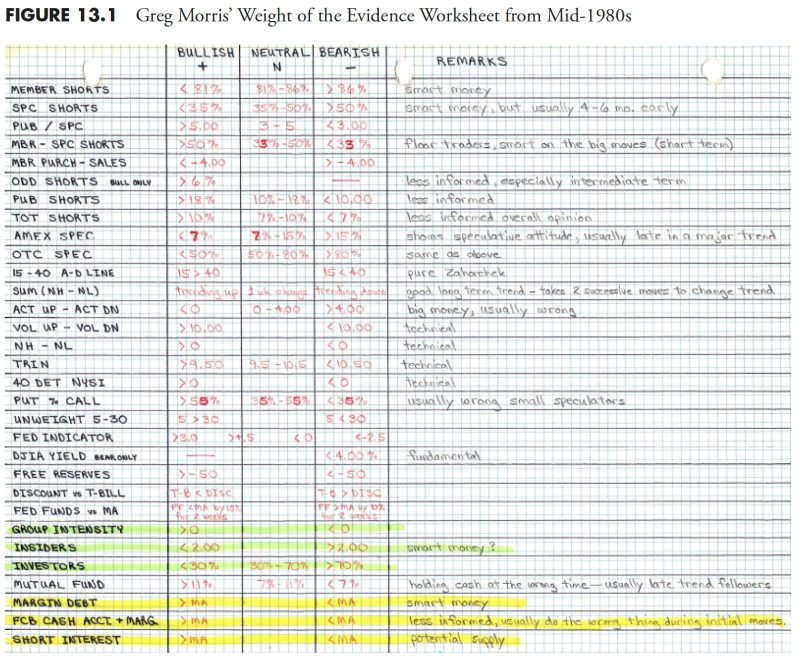
Market measurement is a critical component of money management as it provides valuable insights into market trends, volatility, and potential investment opportunities. By analyzing market data and performance metrics, investors can make informed decisions regarding their investments and portfolio allocations.
One of the key principles of measuring the market is tracking market indices, such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, or NASDAQ. These indices serve as benchmarks for overall market performance and provide valuable information on the direction of the market as a whole. By monitoring these indices regularly, investors can gauge the health of the market and make adjustments to their investment strategies accordingly.
Another important aspect of market measurement is analyzing market volatility. Volatility refers to the degree of variation in market prices over a specific period. High volatility indicates greater price fluctuations, which can present both risks and opportunities for investors. By understanding market volatility, investors can adjust their risk tolerance and investment timelines to better align with market conditions.
In addition to tracking market indices and volatility, measuring market breadth is another vital aspect of money management. Market breadth refers to the number of stocks participating in a market upswing or downturn. A broad market rally, where a significant number of stocks are advancing, typically indicates a healthy market trend. Conversely, a narrow market rally, with only a few stocks driving the market higher, may signal a weaker market trend. Monitoring market breadth can help investors identify potential market reversals and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Furthermore, analyzing market sentiment is crucial for measuring the market effectively. Market sentiment reflects the overall mood and attitude of investors towards the market. Bullish sentiment, characterized by optimism and confidence, often leads to rising stock prices. Conversely, bearish sentiment, marked by pessimism and fear, can result in declining stock prices. By gauging market sentiment through various indicators such as surveys, sentiment indices, and news coverage, investors can gain valuable insights into market psychology and make more informed investment decisions.
In conclusion, measuring the market is an integral part of a rules-based money management strategy. By tracking market indices, volatility, breadth, and sentiment, investors can stay informed about market trends, assess risks and opportunities, and make well-informed investment decisions. Incorporating market measurement into a comprehensive money management framework can help investors navigate the uncertainties of the market with greater confidence and discipline.